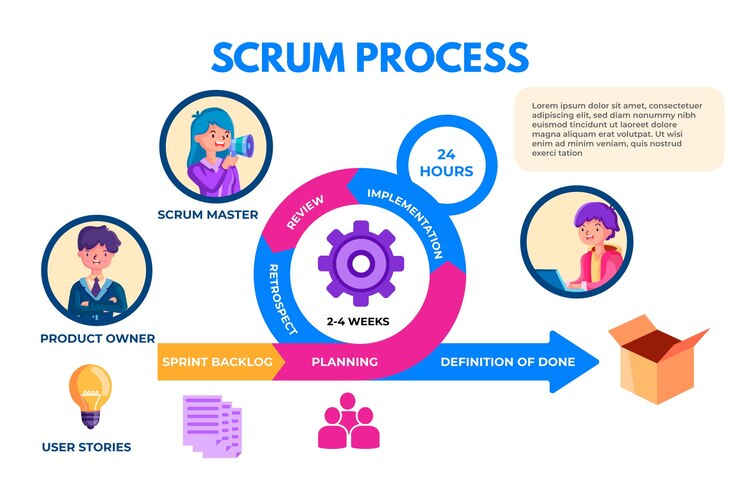
In the fast-paced realm of agile project management, Scrum stands out as a widely adopted framework known for its flexibility and adaptability. At the heart of Scrum lie the teams, and when these teams collaborate closely, they form what is known as “interdependent teams.”
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the world of interdependent teams in Scrum, exploring their significance, dynamics, and the advantages they offer in the pursuit of project excellence.
Understanding Interdependent Teams
Interdependent teams in Scrum are groups of individuals who work closely together on different aspects of a project but share a common goal. These teams understand that their contributions are intertwined, and success hinges on their collective effort. Unlike independent teams that operate in isolation, interdependent teams actively collaborate, communicate, and coordinate their work.
The Significance of Interdependent Teams
- Enhanced Collaboration. Interdependent teams thrive on collaboration. They break down silos and foster a culture of open communication. Team members collaborate on various project aspects, share knowledge, and provide support when needed. This synergy leads to improved problem-solving and innovative solutions;
- Efficient Resource Utilization. In Scrum, resources are often limited, and optimal resource utilization is crucial. Interdependent teams maximize resource efficiency by aligning their efforts. They ensure that skills and expertise are applied where they matter most, avoiding duplication of work and reducing wastage;
- Agile Adaptability. The agile philosophy of Scrum revolves around adaptability and responsiveness to change. Interdependent teams are inherently agile as they can swiftly adapt to evolving project requirements. This adaptability is a competitive advantage in today’s dynamic business landscape.
Dynamics of Interdependent Teams
Cross-Functional Expertise
Interdependent teams are characterized by a diverse skill set. Team members possess a range of skills and expertise relevant to their project area. This diversity allows for comprehensive coverage of project tasks and ensures that no critical aspect is overlooked.
Synchronization
Synchronization is the hallmark of interdependent teams. They synchronize their activities and dependencies to maintain a cohesive workflow. This alignment prevents bottlenecks and ensures that tasks progress smoothly from one team to another.
Clear Communication
Clear and effective communication is the lifeblood of interdependent teams. Team members regularly update each other on progress, challenges, and changes in project requirements. This transparency minimizes misunderstandings and promotes a shared understanding of project goals.
Advantages of Interdependent Teams in Scrum
Improved Efficiency
Interdependent teams streamline project workflows, resulting in improved efficiency. Tasks are completed more swiftly, reducing project timelines and time-to-market for products and services.
Enhanced Problem Solving
Collaborative problem-solving is a forte of interdependent teams. When issues arise, multiple perspectives come into play, leading to more robust solutions. The collective intelligence of the team often outperforms individual efforts.
Flexibility and Adaptability
Interdependent teams are agile by nature. They can quickly adapt to changes in project scope or priorities. This flexibility enables organizations to respond promptly to market dynamics and customer needs.
Quality Assurance
With cross-functional expertise and shared responsibility, interdependent teams maintain a high level of quality in project deliverables. They uphold rigorous quality standards, ensuring that the final product meets or exceeds expectations.
Challenges and Mitigations
While interdependent teams offer numerous advantages, they also face specific challenges that must be addressed:
Communication Breakdowns
Mitigation: Regular team meetings, clear communication channels, and the use of collaboration tools can help bridge communication gaps.
Task Dependencies
Mitigation: Careful task planning, dependency identification, and contingency planning can minimize the impact of task dependencies.
Conflict Resolution
Mitigation: Establishing a conflict resolution process and promoting a culture of constructive feedback can resolve conflicts effectively.
Implementing Interdependent Teams in Scrum
To harness the benefits of interdependent teams in Scrum, organizations need to take specific steps to implement this collaborative approach effectively.
- Team Formation. Begin by carefully selecting team members with complementary skills. Cross-functional diversity is key to ensuring that the team can handle various aspects of the project. Encourage team members to get to know each other and build trust;
- Define Roles and Responsibilities. Clearly define the roles and responsibilities of each team within the interdependent structure. Ensure that every team understands its contribution to the overall project and how it impacts other teams;
- Task Planning and Dependency Mapping. Detailed task planning is essential to identify dependencies between teams. Create a visual map of task dependencies to ensure that teams are aware of their interconnections. This clarity helps prevent bottlenecks and delays;
- Agile Practices. Adopt agile practices such as daily stand-up meetings, sprint planning, and sprint reviews. These practices enhance collaboration and keep teams aligned with project goals. They also provide a platform for discussing issues and adjusting strategies in real-time;
- Communication and Transparency. Promote a culture of open communication and transparency. Encourage team members to share updates, challenges, and successes. Use digital collaboration tools to facilitate communication, especially in geographically distributed teams;
- Agile Leadership. Leadership plays a crucial role in supporting interdependent teams. Agile leaders should empower teams to make decisions, remove obstacles, and provide guidance when needed. They should also act as advocates for the teams within the organization.
Case Study: The Success of Interdependent Teams
To illustrate the effectiveness of interdependent teams in Scrum, let’s consider a real-world case study.
Company X, a software development firm, was facing challenges in delivering projects on time and meeting client expectations. They decided to implement interdependent teams within their Scrum framework. Each team was responsible for specific project components, and they collaborated closely throughout the development process.
The results were impressive:
- Projects were delivered ahead of schedule;
- Client satisfaction ratings soared;
- Cross-functional expertise led to innovative solutions;
- Communication breakdowns were virtually eliminated;
- Quality assurance improved significantly.
Company X’s success demonstrates how interdependent teams can transform project outcomes and drive business excellence.
Embracing the Future with Interdependent Teams
As organizations navigate the ever-evolving landscape of project management, interdependent teams in Scrum emerge as a beacon of collaborative success.
They embody the agile principles of adaptability, transparency, and customer focus, making them a strategic asset for businesses seeking to thrive in a competitive environment.
Embracing interdependent teams requires a commitment to fostering collaboration, investing in team development, and embracing agile practices. The rewards, however, are well worth the effort.
With interdependent teams, organizations can navigate complexity, innovate with confidence, and achieve excellence in the dynamic world of Scrum.